
The Segond Fracture Is an Avulsion of the Anterolateral Complex. Humza Shaikh, Elmar Herbst, Ata Amir Rahnemai-Azar, Marcio Bottene Villa Albers, Jan-Hendrik Naendrup, Volker Musahl, James J. Imaging differential considerations include:Īrcuate sign: avulsion fracture of the head of the fibula 5 History and etymologyįirst described by Paul Ferdinand Segond, French surgeon (1851-1912) based on cadaveric experiments 1,2,4. Spontaneous healing of the Segond fracture may occur following ACL reconstruction 11 and is associated with a particular bone excrescence arising below the lateral tibial plateau. Associated injuries include 1,3:Īvulsion of ACL from the tibial attachment: rareĪvulsion of fibular attachment of the long head of biceps femorisĪvulsion of the fibular collateral ligamentĪlthough the fracture itself is small, the extensive ligamentous injury associated with it usually requires surgical intervention, to correct anterior rotational instability 4. Disruption of the ACL is the most common, however, there are additional frequently encountered injuries. MRI is essential in all cases of Segond fractures to identify internal derangement. This has been referred to as the lateral capsular sign 1, which is best seen on the anteroposterior view of the knee. The classical appearance of a Segond fracture is that of a curvilinear or elliptic bone fragment projected parallel to the lateral aspect of the tibial plateau. They were unable to demonstrate attachment to the ALL. However, the ALL is inconsistently identified on MRI 7.Ī 2017 MRI study of 36 Segond fractures associated with ACL injury showed that the fracture fragment is almost always attached to the posterior fibers of the ITB and the lateral capsule 12. In 2017, the ALL expert group released a consensus paper 8 recognizing the presence of the anterolateral ligament 9 , and noted a constant attachment to the lateral meniscus. Other candidate structures include the iliotibial band and anterior oblique band of the fibular collateral ligament 3. The conventional teaching has been that it is the result of avulsion of the middle third of the lateral capsular ligaments 7.
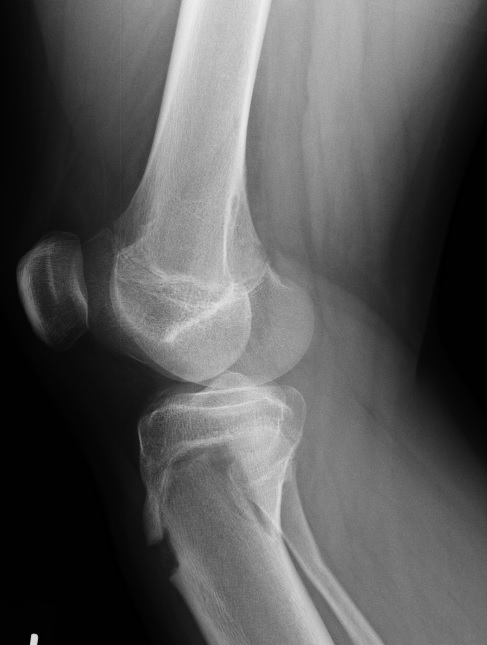
Somewhat surprisingly, the exact cause of a Segond fracture continues to be contentious.
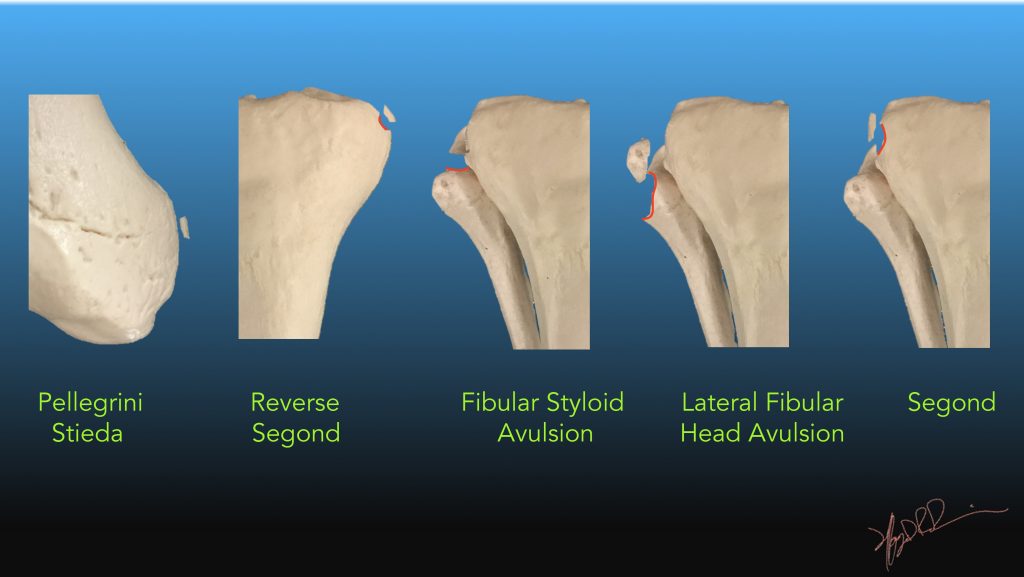
Sports: especially soccer, skiing, basketball and baseball 4,10 Typically these injuries are seen in two settings: Contrary to the more common causes of an ACL tear, which typically involves valgus stress 3, a Segond fracture usually occurs as a result of internal rotation and varus stress 1,4.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
